Describe the Structure of a Synovial Joint Use This Description
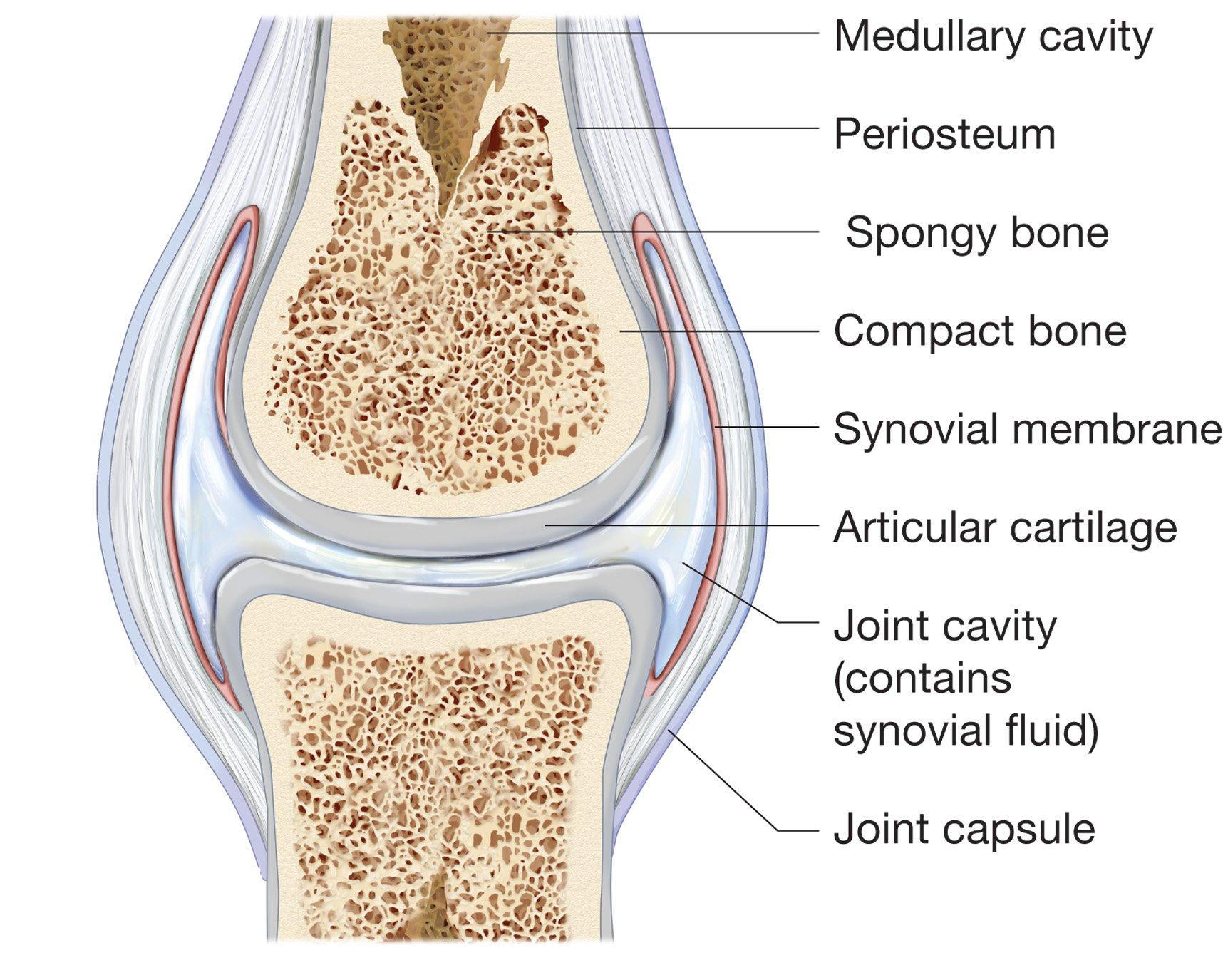
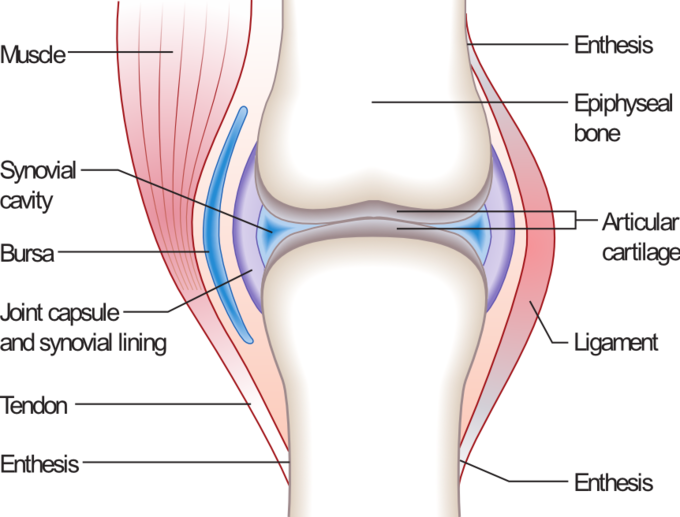
The articular capsule surrounds the joint and is continuous with the periosteum of articulating bones. A synovial joint is a connection between two bones consisting of a cartilage lined cavity filled with fluid which is known as a diarthrosis joint.

Ever Wonder What Is A Synovial Joint 3d Muscle Lab
Circumduction is the movement of a limb in a circular motion as in swinging an arm around.

. Synovial joints give the body many ways in which to move. The bones of a synovial joint are covered by a layer of hyaline cartilage that lines the epiphyses of joint ends of bone with a smooth slippery surface that does not bind them together. Synovial joints are made up of five classes of tissues.
A synovial joint is the type of joint found between bones that move against each other such as the joints of the limbs eg. Characterized by cartilage connecting the bony portions 6. These joints can be found between your upper and lower arm bones otherwise called your elbow as well as your ankles fingers toes and knees.
A Clinical Handbook 2018. Other types of joint allow little or no movement including fibrous joints eg between the bones of the skull and cartilaginous joints eg. Synovial joints are enclosed by a fibrous connective tissue capsule lined with a smooth synovial membrane.
The skeletal system has a number of different joint types for example there are fibrous joints and there are cartilaginous joints. The six types of synovial joints are the pivot hinge saddle plane condyloid and ball-and. Based on structure and functions joints have been further classified into different types.
The articular surface in the condylar joint consists of two distinct condyles that fit with each other. Next lets focus on hinge joints shown as letter B on the diagram. Structure and Components of the Synovial Joints.
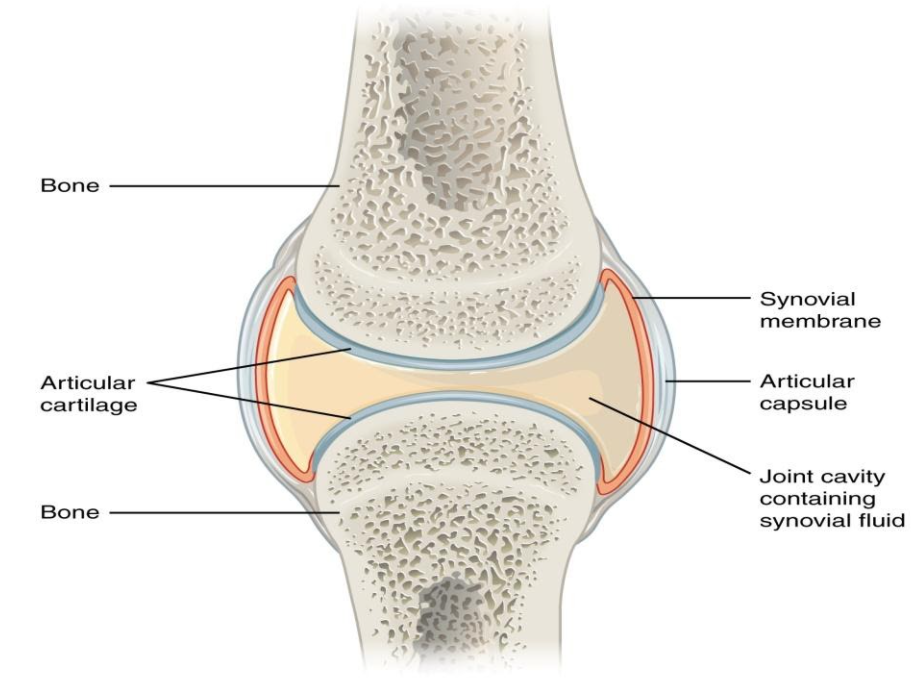
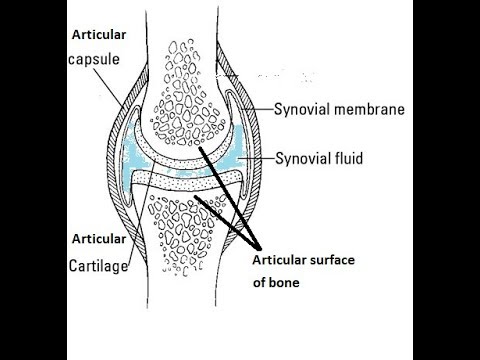
The articulating ends of bones in a synovial joint are covered with articular cartilage and are separated by a cavity that contains synovial fluid. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. All characterized by a fibrous articular capsule lined with a synovial membrane.
Synovial Joint Definition. The joint is surrounded by an articular capsule that defines a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid. This type of joint.
The synovial lining in the bursae and tendon sheaths similar to that within joints is a slippery non-adherent surface allowing movement between planes of tissue. In synovial joints the ends of the bones are covered with cartilage called articular cartilage which cushions the joint and prevents friction and wear. Correctly pair the class of synovial joint with its description.
The fifth one under the types of synovial joints is condylar joint. Bone cartilage synovium synovial fluid and tensile tissues composed of tendons and ligaments. Lin-Fen Hsieh in Braddoms Rehabilitation Care.
At synovial joints the articular surfaces of bones are covered with smooth articular cartilage. The three main features of a synovial joint are. Characteristically it has a joint cavity filled with fluid.
A b Flexion and extension motions are in the sagittal anteriorposterior plane of motion. It also absorbs synovial fluid. I articular capsule ii articular cartilage iii synovial fluid.
Synovial joints also termed diarthrotic joints have a fibrous capsule that connects two bones or cartilage and connects to the periosteum of the two bones. Joints are formed where bones come together. Diarthrosis joints are the most flexible type of joint between bones because the bones are not physically connected and can move more freely in relation to each other.
Typically allows a slight degree of movement 2. The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage. Essentially immovable joints 4.
Has the presence of a space called synovial cavity between the articulating bones which allows a joint to be freely movable. The synovial joint is characterized by its mobility as these joints are able to move freely in multiple planes. These movements take place at the shoulder.
This articular cartilage functions to absorb shock and reduce friction during movement. The structure and function of synovial joints is our second dash point under the skeletal system. You are allowed to ignore this though as you only need to know about the synovial joints which.
Sutures are the most remembered examples 5. Hinge joints are the synovial joint type referred to in our introductory section. Includes joints between the vertebral bodies and the pubic symphysis 3.
Synovial joints allow for smooth movements between the adjacent bones. One is a convex surface which fits perfectly into the concave surface this structure is called condyles. Joints can be simply defined as articulations of bones which functions by providing shape to the skeleton system protects bones by holding them together securely and also helps in movement.
Angular and rotational movements. Hinge joints operate just like the hinges on a door. The articulating surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of articular cartilage.
Shoulder hip elbow and knee. Its function is to protect the ends of the bones and help lubricate joint movement. The joint is surrounded by an articular capsule that defines a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid.
Figure 941 Synovial Joints. A synovial joint is one among the three types. Synovial joints allow for smooth movements between the adjacent bones.
Synovial joints are made up of five classes of tissues. Also known as Articular cartilage this is a smooth tough shiny cartilage which covers the ends of bones. It consists of two layers.
Between the ribs and. Synovial joints allow for smooth movements between the adjacent bones. A synovial joint consists of two bony surfaces that are encompassed by a fibrous capsule with a synovial lining.
Key Structures of a Synovial Joint. Hinge joints are the synovial joint type referred to in our introductory section. These joints can be described as planar hinge pivot condyloid saddle or ball-and-socket joints.
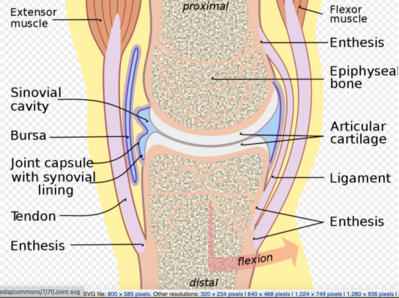
This gives the bones of a synovial joint the ability to move smoothly against each other allowing for increased joint mobility. The joint is surrounded by an articular capsule that. Synovial joints Are united by the dense irregular connective tissue of an articular capsule and often by accessory ligaments.

Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology I

Synovial Joint Structure Teachpe Com
Synovial Joints Anatomy Physiology

Joint The Synovial Fluid Britannica

A Typical Synovial Joint The Knee Joint 19 Download Scientific Diagram

Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology I

The Structure Of A Synovial Joint Synovial Joint Basic Anatomy And Physiology Medical Anatomy

Synovial Joint Easy Pic For Patients To Understand And You Talk About Joint Health Joints Anatomy Synovial Joint Human Anatomy And Physiology

Synovial Joint Anatomy In Animal Definition Types And Structure Anatomylearner The Place To Learn Veterinary Anatomy Online

Figure 8 3 General Structure Of A Synovial Joint Ppt Video Online Download

Describe The Structure Of Synovial Joint With The Help Of A Neat Labelled Diagram

Synovial Joint Diarthrosis Definition Types Structure Examples
Structure And Function Of Synovial Joints Hsc Pdhpe

Synovial Joints Structure Function Types Study Com
Describe A Typical Synovial Joint With A Neat Labeled Class 11 Biology Cbse
Comments
Post a Comment